
source : https://www.labeuropa.eu/
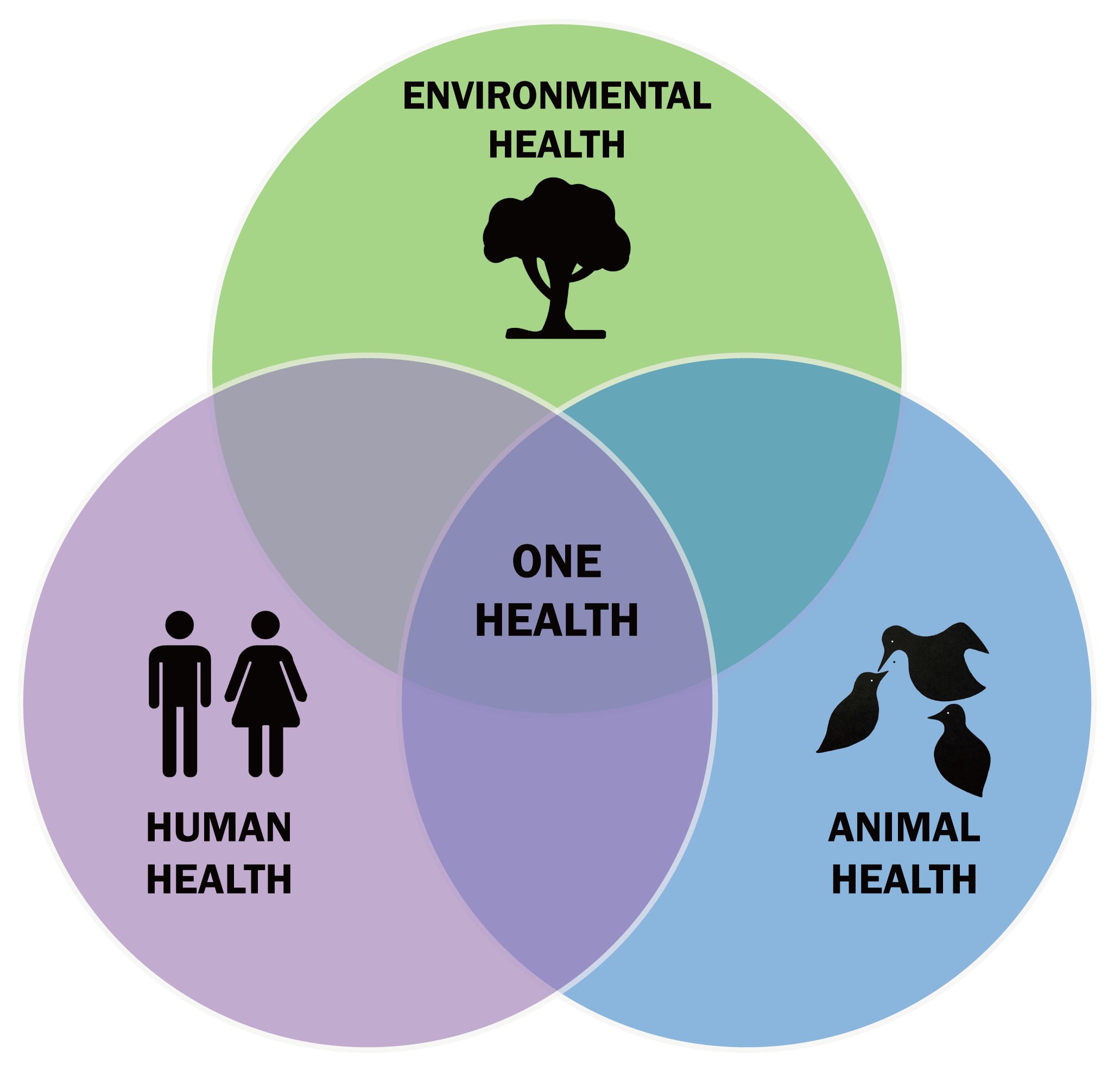
In this modern era, complex health challenges are increasing rapidly. Climate change, urbanization, changing consumption patterns and other factors have contributed to the spread of new diseases and increased antimicrobial resistance. To meet this challenge, the One Health approach has been recognized as an effective strategy. This approach integrates human, animal and environmental health in one holistic framework. In an effort to strengthen the One Health approach, building a laboratory equipped with the latest technology is important.
The Role of Laboratories in the One Health Approach
Laboratories dedicated to the One Health approach play a critical role in understanding, diagnosing, and monitoring diseases that can be transmitted between humans and animals. This laboratory is equipped with advanced technonolgy equipment for microbiology (bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi), and genetics analysis which enables fast and accurate identification of pathogens and diseases. In addition, this laboratory also facilitates interdisciplinary research, enabling collaboration between human health experts, veterinarians and environmentalists.
In the One Health approach, the laboratory has a very important role. Laboratories can provide the following benefits under a One Health approach:
1. Disease Diagnostics
Laboratories play a key role in detecting, identifying and confirming diseases in humans, animals and the environment. Through the analysis of samples from various sources, laboratories can assist in the diagnosis of infectious diseases, including zoonotic diseases, which can be spread between animals and humans. Accurate diagnostics enable prompt and appropriate intervention to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Disease Detection and Monitoring
Laboratories can assist in the detection and monitoring of infectious diseases, both in animals and humans. Through the analysis of samples such as blood, water, soil, or agricultural products, laboratories can detect pathogens, characterize genetically, and monitor changes in pathogen populations over time. This helps identify disease trends, identify potential outbreaks or pandemics, and guide prevention and control actions.
3. Vaccine Research and Development
Laboratories play an important role in the research and development of vaccines against infectious diseases. Through molecular studies, immunological research, and preclinical trials, laboratories can develop effective and safe vaccines to protect humans and animals against infectious diseases. It also involves collaboration between scientists, human health experts, veterinarians and other researchers.
4. Epidemiological Research
Laboratories can support epidemiological research to understand the spread of disease and associated risk factors. By analyzing samples and data, laboratories can help identify sources of infection, study disease transmission, and evaluate the effectiveness of control measures. Data obtained from the laboratory plays an important role in epidemiological modeling and public health response planning.

source : wikimedia
Laboratories play a key role in the One Health approach. In the detection, diagnosis and monitoring of zoonotic diseases, laboratories make an important contribution in protecting human and animal health. In addition, through research, development of vaccines and pharmaceuticals, laboratories play a role in developing solutions for diseases that are cross-species. Cross-disciplinary collaboration and laboratory-supported data sharing also help drive a holistic One Health approach.
In the face of today’s global health challenges, such as the rapid spread of infectious diseases and environmental changes affecting human and animal health, it is important for laboratories to continuously develop their capacities. This includes the development of more sophisticated laboratory technology, training of skilled workers, and close cooperation with related institutions and organizations.
Through the broad role and importance of laboratories in the One Health approach, we can strengthen efforts to protect human, animal and environmental health. Cooperation and collaboration between the human, animal and environmental health sectors, as well as continued investment in laboratory development, will play a key role in realizing the goal of a better One Health.
Reff :
- The role of veterinary diagnostic laboratories in One Health. Journal of Veterinary Medical Education.
- Emerging infectious diseases: threats to human health and global stability.
- http://www.onehealthinitiative.com
- Karesh, W. B., & Cook, R. A. (2005). The human-animal link. Foreign Affairs, 84(4), 38-50

Leave a Reply