The terms Biosafety and Biosecurity (biorisk) have become known in Indonesia since the emergence of the bird flu virus in Indonesia around 2006. Several trainings have been conducted at several institutions in Indonesia in collaboration with several international institutions. The ministries and institutions that are the main targets are the ministry of health, ministry of agriculture and related institutions. The Ministry of Health initially provided training to the Influenza disease laboratory network and then developed into training for trainers (Training of Trainers, ToT). Biosafety and Biosecurity were introduced along with the emergence of the bird flu virus in Indonesia considering the danger level of the bird flu virus that enters and circulates is in the category of High Pathogenic Pathogen. Biosafety and Biosecurity, or what became known as Biorisk, is a way so that High Pathogenic Pathogens can be handled properly and also not misused for improper purposes, such as crime, terrorism, biological weapons and others.
Biosafety and Biosecurity are two important concepts in scientific research and development to ensure the safety and security of humans, animals and the environment in relation to biological risks. The following is an introduction to biosafety and biosecurity and their importance in scientific research and development:
1. Biosafety
Biosafety is a series of steps and actions designed to protect humans, animals and the environment from biological hazards that may arise as a result of research or work related to microorganisms or potentially hazardous biological materials. Biosafety principles include the use of personal protective equipment, management of biological waste, use of sterilization techniques, control of access to work areas, and risk assessment and mitigation.

source : https://www.iberdrola.com/
2. Biosecurity
Biosecurity is an effort made to prevent, control, and reduce risks associated with access, misuse, or accidental or intentional release of dangerous biological agents. This involves setting up strict policies, procedures and infrastructure to protect potentially hazardous biological materials from falling into unauthorized hands or being used for malicious purposes. Biosecurity involves monitoring access to laboratories, inventory control of biological materials, training of personnel, and protection against security incidents.
The importance of biosafety and biosecurity in scientific research and development:
1. Physical Security
Physical security measures and access restrictions should be tiered depending on the risks involved. Biological materials do not have the same level of physical protection. Group 3 and 4 pathogenic microorganisms require more stringent mitigation measures because they include pathogenic agents with a high level of risk that require a higher level of security.
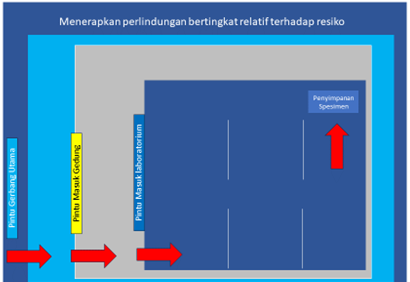
Tiered Physical Security Levels
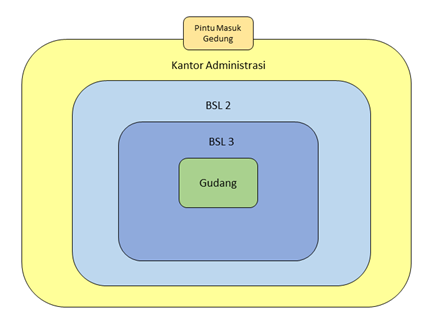
Tiered Physical Security Levels
Physical security goals are known as 3D :
- Deter/Discourage : Does not motivate or provoke criminals who want to access biological materials
- Detect : Detect crimes aimed at accessing biological materials
- Delay: Slows down the process of entering the biological material storage area.
Any physical security system barrier must slow down the achievement of biological material storage areas, for example, fences, guards, doors with access codes. Cameras, security lights, alarms are not barriers because they do not prevent access but these objects are only tools for monitoring while what includes barriers are guards, trained personnel, fences and others. Some examples of implementing physical security are as follows:
a. Limited access implementation
- Use of identification
- Access control: mechanical lock, cardlock, door code, fingerprint, retina scan and others

Restricted access control

Restricted access control
b. Logged access: Visitor logbook
c. System breach detection: alarm, CCTV
2. Personnel Security
VBM safeguards pose unique challenges and require a different approach than handling chemical or radioactive materials because a) The pathogen can replicate and thieves only need to take in very small amounts; b) Neither tool can detect VBM; c) Easy to hide sometimes only in a very small tube,dried or in filter paper; d) There is no system that can track or monitor the amount or volume precisely because in the laboratory it can always change during experiments so it is difficult to know how much someone took.
3. Protection of Human and Animal Health
Biosafety and biosecurity ensures that risks associated with research or development of harmful biological agents are minimized, thus protecting the health of humans and animals involved in such activities. This is important to prevent infection or exposure that could endanger their life and health.
4. Environmental Security
Through appropriate biosafety and biosecurity measures, the risk of spreading microorganisms or potentially hazardous biological materials into the environment can be reduced. This helps protect natural ecosystems and prevent negative impacts on the surrounding flora and fauna.
5. Safety of hazardous biological materials
Biosecurity aims to prevent the misuse of potentially hazardous biological materials for malicious purposes, such as the development of biological weapons or biological terrorism.Hazardous biological accountability procedures should be implemented to track the inventory, storage, use, transfer and disposal of hazardous biological materials. This procedure is also capable of tracking biological materials in the facility, tracing their whereabouts and the person in charge of the biological material so that no material remains in the freezer or storage area when the person in charge is no longer working in the laboratory.
Some of the procedures that can be carried out in the hazardous biological substance accountability program are as follows:
a. Identification of biological materials
b. Appoint person in charge
c. Determine who is given access to the biological material
d. Determine the inventory system
e. Define a documentation system that defines where to store, use, method of storage, transfer and disposal
f. Determine the emergency response system related to the biological material. A reporting system is needed to find out irregularities, missing samples, signs of attempted theft
g. Determine the audit system by developing a policy to review the regular and scheduled inventory system. Reviewing one part of the inventory system is enough to control whether a system is effective or not. Special audits can be carried out in emergencies such as the emergency removal of biological materials due to freezer malfunction.
6. Information Security
Care is required in safeguarding important information so that it is not misused, such as information regarding inventories of VBM or hazardous biological materials, laboratory plans, sensitive research information, diagnostic test results, etc.
a. Personnel need to receive training to determine sensitive information. Several things need to be considered by staff, for example not leaving sensitive information in hardcopy or softcopy unattended, hardcopy keys in a cupboard when not in use, not making photocopies if not needed, only bringing softcopies or hardcopies when given a special assignment and not taking them home and Always be vigilant when disclosing sensitive information.
b. Limited access to sensitive information for researchers who need it.
c. Cybersecurity to protect from hackers who will try to steal information. If it’s on a computer, it needs to be protected with a password.
d. Data should be destroyed when it is no longer needed by always keeping the master data in a safe place.
7. Transportation Security
Samples or waste containing hazardous biological materials often need to be moved to rooms, laboratories or other facilities. In some cases, samples need to be tested in other cities or countries for testing or storage purposes. Hazardous biological materials can be in the form of cultures, patient or animal specimens, infected body parts or organs, biological products such as vaccines or similar therapeutic products, and genetically modified organisms. The transfer of hazardous biological materials has national and international regulations, depending on the country of origin and destination as well as the method of transfer.
Other Advantages of Biosafety and Biosecurity :
In addition to protecting humans and animals from health risks, biosafety and biosecurity also provide other benefits in scientific research and development. Good practice in biosafety and biosecurity improves the quality of research by ensuring the integrity and reliability of the data it produces. In addition, an emphasis on biosafety and biosecurity also helps maintain public confidence in scientific research and development, and prevents the risk of disease spreading to the wider community.
In scientific research and development, biosafety and biosecurity play an important role in protecting human and animal health and preventing the spread of harmful biological agents. Appropriate biosafety and biosecurity practices, such as the use of PPE, sound management of biological waste, control of access to facilities, and management of inventories of hazardous agents, are critical to reducing risk and maintaining safety in research and development activities.
In an effort to achieve these goals, it is important for research institutions and researchers to comply with the regulations and guidelines set by regulatory agencies and related institutions. In addition, ethics and awareness of the social and environmental implications of research must also be important considerations in carrying out biosafety and biosecurity.
By prioritizing biosafety and biosecurity in scientific research and development, we can maintain safety, protect the health of the people and animals involved, and ensure the integrity and trust in science.
Reff :
– World Health Organization. (2004). Laboratory biosafety manual (3rd ed.).
– World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). (2018). OIE biological threat reduction strategy.
– Modul Sistem Manajemen Biorisiko Laboratorium, INDOHUN, OHLN.


Leave a Reply