In the era of globalization and the interconnection between humans, animals and the environment, the management of diseases that can spread between species (zoonoses) is becoming increasingly complex. The One Health concept that integrates human, animal and environmental health is key in addressing public health challenges.The One Health laboratory network plays a central role in detection, monitoring and treatment of zoonoses. This article examines the role of advanced diagnostic technology in enhancing the effectiveness of the One Health laboratory network.
The Importance of Advanced Diagnostic Technology in One Health
Advanced diagnostic technology plays a crucial role in supporting the efforts of the One Health laboratory network. Some of the reasons for the importance of the latest diagnostic technology are:
1. Fast and Accurate Detection
Advanced diagnostic technology enables quick and accurate identification of zoonotic pathogens. This enables a timely and effective response to disease cases. The following are examples of advanced diagnostic technologies playing a critical role in increasing the effectiveness of the One Health laboratory network:
1.1 PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) / RT-PCR (Real Time – Polymerase Chain Reaction) test
PCR technology enables the amplification and detection of genetic material from disease-causing pathogens. PCR is a fast and highly sensitive method for identifying disease-causing microorganisms. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a widely used enzymatic process that allows scientists to replicate specific regions of DNA, resulting in the production of multiple copies of a particular DNA sequence. PCR combines the principles of complementary nucleic acid hybridization and nucleic acid replication to amplify one copy of the target DNA sequence, although it cannot be detected by standard hybridization methods. This amplification process can produce millions to billions of copies of the target DNA in a relatively short time, providing abundant amounts of DNA for further analysis.
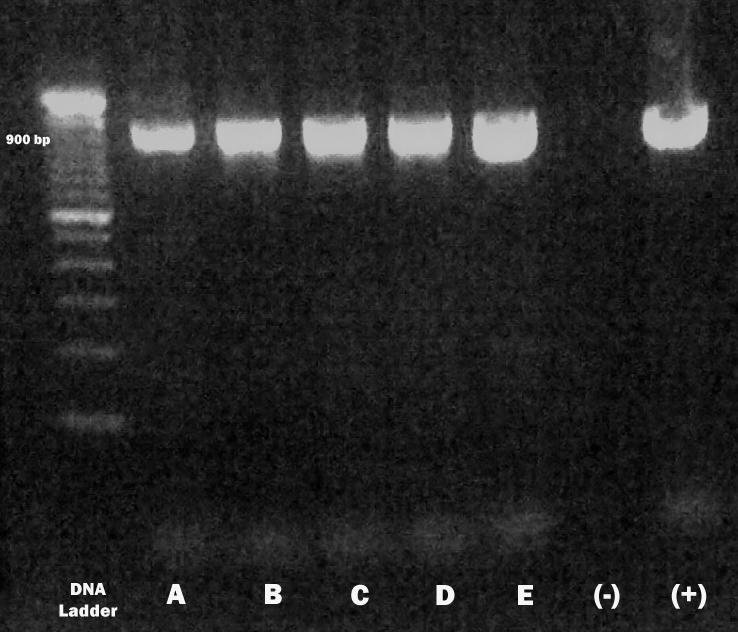
Example of a PCR result ribbon image
- PCR / RT-PCR test usage application:
Rabies virus detected using the RT-PCR method is considered to have high sensitivity and specificity for ante-mortem examination. RT-PCR is an easy method to perform with a faster processing time compared to the FAT (Fluorescent Antibody Test) and MIT (Mouse Inoculation Test). This is an advantage of the RT-PCR method compared to other examination methods so that detection of the rabies virus in human cases suspected of contracting rabies through the bite of a rabies-transmitting animal (GHPR) can be done more quickly.
1.2 Molecular Biology
Molecular biology techniques such as ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) are used to detect antibodies in samples, aiding in disease diagnosis and monitoring. The success of vaccination in animals or humans can be tested using ELISA. This method is one of the methods used to detect rabies antibodies in animal (dog) serum and human serum. The ELISA method is also very useful for detecting antibodies related to epidemiological surveys in large population sizes. This antibody titer is used to confirm the antibody response after vaccination in dogs. Antibodies are special chemicals capable of binding to specific antigens. Specific antibodies can be measured using predefined antigens and this is the basis of many diagnostic biological tests including ELISA. The results of the ELISA test were obtained from absorbance measurements using an ELISA reader.
ELISA Plate
- ELISA application:
The success of rabies vaccination in animals or humans can be tested using ELISA. Serum is taken from a blood sample and put into a microtube for further testing. Serum was inactivated using a water heater for 30 minutes at 56°C. Making a recording sheet aims to determine the location of the control and serum samples in the microplate wells. The test procedure was carried out according to the Indirect ELISA Rabies kit work guide. The reading of the ELISA results uses an ELISA reader with two filters, namely the wavelength of 450 nm and 620 nm as a reference. The result of the reading using an ELISA reader is in the form of a value (Optical Density) or absorbance. The absorbance is presented in the form of a standard/calibration curve to determine the relationship between concentration and absorbance.
1.3 NGS (Next-Generation Sequencing) Technology
NGS is a sophisticated and fast method of genome sequencing, enabling in-depth analysis of the genetic data of various pathogens.
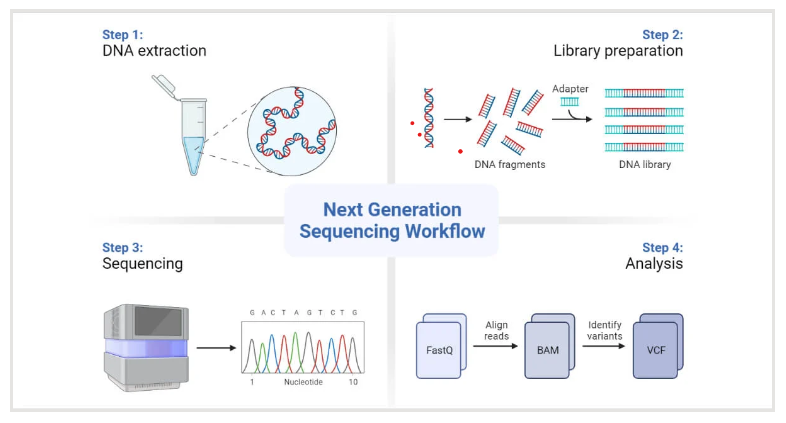
NGS Workflow
- NGS usage applications:
Genomic surveillance with NGS can track transmission of infectious diseases and identify new strains of coronaviruses and other emerging pathogens. With nearly complete pathogen genome sequence data, we can implement effective infectious disease surveillance strategies to help prevent further transmission and infection.
Surveillance of infectious diseases with NGS can:
– Tracing the routes of transmission of infectious diseases globally
– Determines how quickly a pathogen like the coronavirus mutates as it spreads
– Identify new and known mutations in pathogens such as coronaviruses, influenza A & B, and others
– Infectious disease therapy resistance studies
– Investigate vaccine avoidance mechanisms
Genome surveillance helps public health officials trace epidemic pathways, carry out contact tracing, determine the evolutionary level of a pathogen, and understand whether a pathogen is changing in a way that could affect diagnostic or therapeutic effectiveness.
2. Laboratory Capacity Building
With the existence of sophisticated technology, laboratories can increase the capacity and quality of their diagnostic services. More reliable and accurate test results can be provided, strengthening the laboratory’s credibility. Using advanced diagnostic technology within the One Health laboratory network requires strong resources and collaboration. Some important steps that need to be taken are:
- Investment in Resources : Governments and health agencies should allocate sufficient resources to update laboratory technology.
- Workforce Training : Well-trained human resources are the key to effectively operating advanced diagnostic technology.
- Collaboration Network : One Health Laboratories should collaborate with other health institutions, research institutions, and environmental agencies to share knowledge and data and build capacity together.
3. More Efficient Epidemiological Investigations
Epidemiological investigations are increasingly efficient thanks to the critical role advanced diagnostic technologies play in increasing the effectiveness of the One Health laboratory network. The integration of technologies such as high-speed PCR, genome sequencing methods, and rapid detection tools has allowed researchers to quickly identify disease-causing agents and track their distribution patterns. This leads to faster and more appropriate responses to disease outbreaks, as well as a better understanding of the relationship between human, animal health and the environment. The combination of data from humans, animals and the environment generated by this technology also helps in understanding disease transmission patterns and risk factors, thereby supporting more effective disease prevention and control efforts.
4. More Effective Disease Control
Advanced diagnostic technologies allow laboratories to more effectively monitor and control changing disease trends. This helps detect spikes in disease cases and implement preventive measures before outbreaks spread.
Advanced diagnostic technology has a crucial role to play in increasing the effectiveness of the One Health laboratory network. With advanced diagnostic technology, laboratories can detect disease quickly, provide high-quality diagnostic services, and assist in effective disease surveillance and monitoring. With strong collaboration and good resource management, advanced diagnostic technologies can be highly effective tools in One Health’s efforts to protect human, animal and environmental health. Data generated from this technology can be quickly integrated and analyzed to identify patterns of disease spread, measure their impact, and design more effective control strategies. With the connectivity between human laboratories, animals and the environment through this technology, disease surveillance becomes more holistic and responsive to public health threats.
Source :
- Lequin RM. 2005. Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)/ Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Clin Chem 51(52): 2415-2418.
- Morse, S., Mazet, J., Woolhouse, M., et al. (2012). Prediction and prevention of the next zoonotic pandemic. The Lancet, 380(9857), 1956–1965.
- Mukrimaa, SS, Nurdyansyah, Fahyuni, EF, YULIA CITRA, A., Schulz, ND, غسان, د., … Harmianto, S. (2016). No主観的健康感を中心とした在宅高齢者における 健康関連指標に関する共分散構造分析Title. Journal of Elementary School Teacher Education Research, 6(August), 128.
- Santoso, K., Herowati, UK, Rotinsulu, DA, Murtini, S., Ridwan, MY, Hikman, DW, … Sukmawinata, E. (2021). Comparison of Colorimetric-Based Rabies Antibody Titer Detection Using ELISA reader and Mobile Phone Camera. Veterinary Journal, 22(1), 79–85.
- Setiaji G, Agustini NLP. 2011. Study of rabies antibody responses in post-vaccinated dogs on the island of Bali. Veterinary Bulletin 13(78): 36- 44.
- Teixeira, M., Costa, M., de Oliveira, D., et al. (2020). One Health approach: A systematic review of diagnostic modalities for major neglected zoonotic diseases in low- and middle-income countries. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 96, 440-448.
- Woolhouse, M., Scott, F., Hudson, Z., et al. (2012). Human viruses: discovery and emergence. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 367(1604), 2864–2871.
- Xu G, Weber P, Hu Q, Audry L, Li C, Wu J, Bouhy H. 2007. A simple sandwich ELISA for the detection of lyssavirus necleocapsid in rabies suspected specimens using mouse monoclonal antibodies. Biologicals 35: 297- 302.
- https://microbiologynote.com/id/polymerase-chain-reaction-pcr-steps-principle-application/


Leave a Reply