Definition of Rabies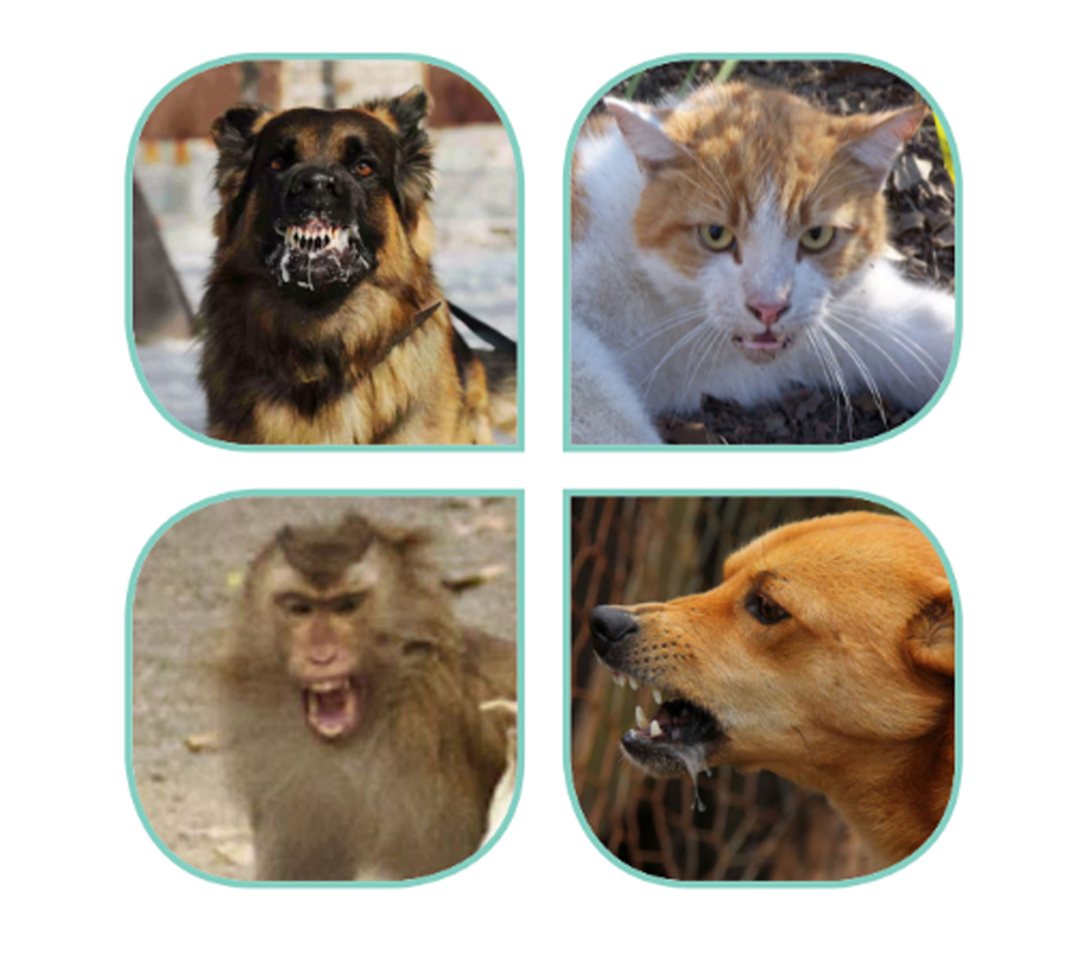
Rabies is a zoonotic disease, a disease that is transmitted from animals to humans. This infection is transmitted by animals infected with rabies. The main animals that cause the spread of rabies are dogs, bats, cats and monkeys. In Indonesia, rabies or what is known as “mad dog disease” is still a problem that threatens public health. This disease is caused by the rabies virus and can be transmitted from animals to humans through the bites or scratches of infected animals. Rabies (mad dog disease) is an acute infectious disease, attacking the central nervous system caused by Lyssavirus. The rabies virus can be transmitted through saliva, bites or scratches and licks on broken skin by animals infected with rabies. Animals that are at high risk for transmitting rabies are generally wild animals or pets that have not received the rabies vaccine.
Rabies Incubation Period
Symptoms of the incubation period of the rabies virus ranges from 4 – 12 weeks, after the incubation period a person infected with the rabies virus will experience flu-like symptoms, fever, muscle weakness, tingling or burning sensation in the bite area, pain or headache, fever, nausea and vomiting, feeling restless, confused or threatened without any cause, hyperactivity, hallucinations, insomnia or sleep disturbances, difficulty swallowing when eating or drinking and excessive saliva production. Symptoms of rabies in humans develop gradually starting with flu-like initial symptoms and progressing to severe neurological disorders. Even though it can be fatal, patients still have a chance of recovery as long as they are treated immediately after being exposed to the rabies virus.
Measures to prevent rabies virus infection by reducing risk factors by :
- Vaccinating rabies in pets.
- Get yourself a rabies vaccine.
- Maintain contact with animals that have the potential to have the rabies virus
- Keep pets from interacting with wild or foreign animals
- Report to the health officer if you meet a person or animal that has symptoms of rabies.
- Prevent other animals that have the potential to spread rabies from entering the house.
Rabies Cases in Indonesia in 2023
The Indonesian Ministry of Health (MoH) announced that there were 11 cases of death caused by rabies. 95% of rabies cases are caused by dog bites. 95% of cases of rabies in humans are acquired through the bite of an infected dog. There are also a variety of wild animals that act as virus reservoirs on various continents such as foxes, raccoons and bats, but 95% are due to dog bites,” said the Director of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control dr. Imran Pambudi, MPHM at a virtual press conference, Friday (2/6).
As of April 2023, there have been 31,113 cases of bites by rabies-transmitting animals, 23,211 cases of bites that have received anti-rabies vaccines, and 11 cases of death in Indonesia. Currently there are 26 provinces that are endemic to rabies but only 11 provinces that are free of rabies, namely the Riau Archipelago, Bangka Belitung, DKI Jakarta, Central Java, DI Yogyakarta, East Java, West Papua, Papua, South Papua, Central Papua and Highlands Papua.
There have been two districts that declared rabies extraordinary events (KLB), namely Sikka District, NTT and South Central Timor District (TTS). The rabies situation in Indonesia from 2020 to April 2023, an average of 82,634 bite cases per year, then nearly 57,000 people who were given the anti-rabies vaccine.
What are the characteristics of Rabies in humans ?
Fever, nausea, sore throat, severe headache, restlessness, fear of water (hydrophobia), fear of light (photophobia), excessive salivation (hypersalivation).
What are the characteristics of Rabies in dogs ?
- Violent Type Dog
- The voice becomes hoarse
- Not obeying the employer’s orders
- Biting and attacking anything that moves/found
- Run aimlessly
- Forgot to go home
- Fight not to be outdone
- The tail is between the two thighs
- Convulsions followed by paralysis
- Usually dies within 4-7 days after the first symptoms appear
- Calm Type Dog
- Hide in a dark and cool place
- Unable to swallow
- Mouth open
- Excessive salivation
- Seizures are brief and often invisible
- Paralysis
- Death occurs in a short time
First aid :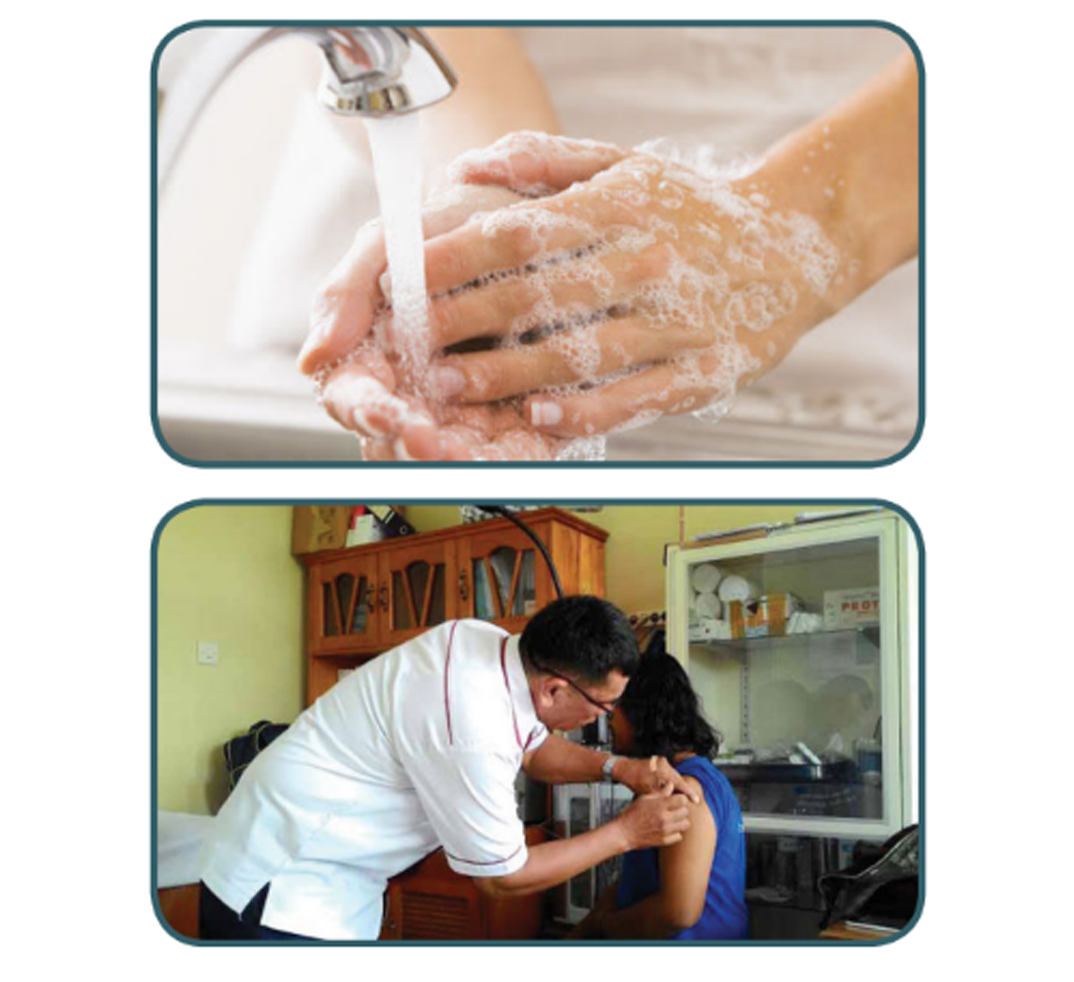
As a first aid measure if someone is bitten by a rabies-transmitting animal such as a dog. The way to treat bite wounds from rabies-transmitting animals is to wash the bite wound as soon as possible with running water and soap for 15 minutes and then give an antiseptic. The next step is to immediately take to the hospital to wash the wound again and get the Anti-Rabies Vaccine (VAR) and Anti-Rabies Serum (SAR). Treating the wound as soon as possible is effective in preventing symptoms and death.
Efforts that have been made in controlling Rabies in Indonesia:
- Coordinate regularly with cross ministries/agencies through the one health approach
- Provide guidelines for controlling rabies for all primary and secondary health facilities
- Train zoonoses program managers from both the human, animal and wild animal health sectors
- Provide logistics needs in the form of Anti-Rabies Vaccine (VAR) and Anti-Rabies Serum (SAR)
- Provide information and educational communication (IEC) media for all primary and advanced health facilities
- Carry out an integrated epidemiological investigation (human, animal and wildlife health sector) if there is an increase in cases/outbreaks
- Conduct surveillance on humans through the Early Alertness and Response System
- Establish a Rabies Center.
Linkage Between Animal and Human Health in Rabies Transmission
Rabies is a clear example of how animal and human health are linked. The rabies virus is transmitted among animal populations, such as dogs, cats, foxes, and bats. When humans interact with animals infected with rabies, especially through bites or scratches, the virus can enter the human body and cause serious infections of the nervous system. Efforts to control rabies cannot be separated from efforts to prevent and control the animal population. This disease can continue to spread if the reservoir animals are not managed properly, and awareness of the importance of animal health in preventing rabies transmission is crucial.
The Importance of Cross Sector Collaboration
In recent years, the concept of One Health continues to be echoed at the global level. One Health in essence is how we can prevent and control disease seen from 3 aspects, namely human, animal and environmental health aspects. When we tackle rabies, of course we can’t just focus on the livestock sector or the animal health side, by vaccinating dogs. On the other hand, we need to provide education to the public about giving vaccines to their pet dogs, maintaining a healthy environment, and ensuring that the public can access medication or therapy due to dog bites, so that the transmission of rabies can be controlled.
Permenko PMK No. 7 of 2022 has a close relationship with the socialization of zoonoses. Permenko PMK No. 7 of 2022 is a regulation of the coordinating minister which aims to regulate procedures for the management of zoonotic diseases in Indonesia. In this regulation, there are provisions governing the supervision, prevention, control and handling of zoonotic diseases so that they can be managed more effectively. In addition, this regulation also includes steps that must be taken by related agencies, both from the health, agriculture and environmental sectors, to increase cooperation in the management of zoonotic diseases. this will be widely informed to the public, breeders, health workers, and other related parties. This Permenko PMK needs to be socialized with the aim of increasing public awareness about the dangers of zoonotic diseases, how they are transmitted, and prevention efforts that can be taken. Permenko PMK No.7 of 2022 also provides information on preventive measures that must be taken by the public, including in dealing with outbreak situations or extraordinary events due to zoonoses. Proper information dissemination will help the public to recognize the early signs of a zoonotic disease, so that they can immediately seek medical help and prevent further spread.
Refers to the coordinating ministerial regulation, wildlife trade and conservation also need to be upheld. The government needs a comprehensive strategy to continue socializing zoonotic risks based on local wisdom, by involving the local community. Monitoring or surveillance of the emergence of new infectious diseases also needs to be strengthened. Research related to health, infrastructure improvement and preparedness in dealing with new infectious diseases, and research related to medicines require collaboration not only at the national level, but at the global level.
Rabies control requires close collaboration between various sectors, including animal health, human health, agriculture, government, and society. The following are the reasons why this cross-sector collaboration is very important :
1. Prevention and Control of Animals
The involvement of veterinary experts in monitoring and regularly vaccinating animals is an important step to prevent the spread of rabies. Mass vaccination programs for potential reservoir animals can reduce the risk of rabies virus transmission to humans.
2. Public Education and Awareness
Collaboration with the human health sector helps raise public awareness about the risks of rabies and the importance of seeking medical care after a bite from an animal suspected of having rabies. Proper education can help people recognize the early signs of rabies and report immediately to the authorities for further action.
3. Role of Government:
Government involvement in formulating policies and regulations related to rabies is very important. Cross-sectoral coordination assists in distributing resources, strengthening vaccination programmes, and strengthening case reporting systems for rapid response actions.
INDOHUN Collaboration in Facing Real Threats of Zoonoses and Emerging Infectious Diseases 
INDOHUN, which stands for Indonesian One Health University Network, played an active role in the formulation of PERMENKO Number 7 of 2022 concerning Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Zoonoses and New Infectious Diseases (PIB). With a high commitment to the One Health approach, INDOHUN has contributed significantly to formulating policies aimed at preventing and controlling the spread of zoonotic diseases and new infectious diseases in Indonesia.
As a university network that focuses on a holistic health approach, INDOHUN has collaborated with various parties, including the government, international health organizations, and academic institutions, to provide the latest insights and data on health issues related to zoonoses and EIDs. With the support of reliable experts and researchers, INDOHUN plays an important role in providing scientific input which forms the basis for the formulation of these regulations.
Not only involved in formulating policies, INDOHUN was also given the opportunity to become a moderator in launching PERMENKO Number 7 of 2022 at the Heritage Building of the Coordinating Ministry for Human Development and Culture (Kemenko PMK) on March 8 2023. In this role, INDOHUN brought stakeholders together, including experts, academics, medical personnel, and the general public, to discuss and collaborate in efforts to prevent and control zoonoses and EIDs.
INDOHUN’s active participation in the formulation of PERMENKO Number 7 of 2022 and its role as moderator in the Kemenko PMK Heritage Building shows their commitment to bridging the gap between science and policy and strengthening cross-sector collaboration to achieve common goals in maintaining public health and environmental sustainability in Indonesia .
Sources :
- https://sehatnegeriku.kemkes.go.id/baca/rilis-media/20230602/3343156/hingga-april-2023-ada-11-kasus-kematian-karena-rabies-segera-ke-faskes-jika-digigit-anjing/
- RMA. Adjid, dkk. Penyakit Rabies di Indonesia dan Pengembangan Tehnik. https://repository.pertanian.go.id
- https://www.antaranews.com/berita/1085380/kolaborasi-hadapi-ancaman-nyata-zoonosis-dan-pie
- https://ayosehat.kemkes.go.id/mengenal-penyakit-rabies


Leave a Reply