One workplace that has a high potential for danger is the laboratory. Laboratories are very important facilities in schools, universities, health facilities, research facilities, and production facilities related to biological materials. Working in a laboratory, one must not act carelessly in treating and using existing equipment and materials in order to reduce the possibility of accidents occurring in the laboratory. Potential dangers that can occur in the laboratory include fire, poisoning, falls or slips, being stabbed by sharp objects, being infected with pathogens, equipment damage, and others.
A hazard is a source, situation, or action that has the potential to cause injury, illness, or a combination of both. Working in a laboratory carries the danger of accidents. Accidents that often occur in laboratories include fire, illness, death, and losses due to accidents or damage to laboratory equipment. To avoid and minimize the possibility of potential hazards occurring in the workplace, recognition of potential hazards in the workplace is the basis for knowing their effects on workers and can be used to carry out control efforts in order to prevent work-related diseases that may occur.
In general, potential hazards in the work environment can originate from various factors, including:
- Technical factors, namely potential hazards that originate or exist in the work equipment used or from the work itself;
- Environmental factors, namely potential dangers originating from or existing in the environment, which can originate from the production process, including raw materials, both intermediate products, and final results;
- The human factor is a potential danger that is quite large, especially if the person doing the work is not in excellent health, both physically and psychologically.
The types of dangers in the laboratory include:
- Fire, as a result of the use of flammable chemicals such as organic solvents, acetone, benzene, ethyl alcohol, ethyl ether, etc.
- Explosion is a result of explosive reactions from reactive materials such as oxidizers.
- Poisoning with dangerous chemicals, such as arsenic, lead, etc.
- Irritation is inflammation of the skin or respiratory tract, as well as the eyes, due to direct contact with corrosive materials.
- Injuries to the skin or eyes due to broken glass, metal, wood, etc.
- Electric shock.
Assessing Physical Hazards
Hazards are the characteristics of a material, the way a tool works, the way a job is done, and the place, position, or conditions of the work environment that can cause damage to property. Occupational diseases, injuries, and temporary and permanent disabilities Nor death. One type of danger that can be encountered in the laboratory is physical danger. Physical hazards include the condition of infrastructure, height, temperature, humidity, pressure, light, electricity, radiation, noise, vibration, and ventilation. The use of machines, work tools, materials, and production processes has become a source of danger that can cause harm. The most important thing is not to run away from the danger that will occur, but to manage the existing danger so that the chance of it happening or the consequences it causes are not large.
Five Preventions of Physical Hazards in the Laboratory:
- Fire Prevention: Properly functioning fire extinguishers are available.
- Electrical hazard prevention:
- Electrical installations are installed in accordance with the provisions for laboratories.
- The interior cable system has a ground (built-in conductor), and the cable is in good condition.
- The circuit breaker panel is placed in an easily accessible location, and the switch is easily marked.
- Maintenance of environmental sanitation:
- All rooms must be clean, dry, and hygienic.
- There are trash bins available that are lined with plastic bags of different colors for each type of waste.
- There is a special place for eating and drinking for laboratory staff.
- Personal protective clothing is available and used when necessary.
- Storage of flammable liquids:
- Liquid containers are made of fire-resistant materials.
- Cabinets or storage shelves are made of strong materials and labeled as non-flammable.
- The storage room is equipped with good ventilation.
Assessing Biohazards (Biological)
Biohazards are something that needs to be considered in laboratories that handle microorganisms or substances contaminated with microorganisms. This danger usually appears in clinical research laboratories, infectious diseases, and chemical research. It does not rule out the possibility of appearing in microbiology laboratories; it may also appear in other laboratories. Biohazard risk assessments need to consider a number of factors, including the organism being manipulated, the changes made to the organism, and the activities that will be carried out with the organism.
Biohazard risk assessments include manipulated organisms and changes made to these organisms. Dangerous biohazard risk assessments need to consider several factors, such as:
- manipulated organisms
- changes made to the organism
- activities that will be carried out with the organism.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is protective equipment used by a worker to protect himself from environmental contamination. PPE, in English, is known as Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). By looking at the word “personal” in the word PPE, every piece of equipment worn must be able to protect the wearer. PPE can range from simple to relatively complete. PPE is the most basic prevention solution for all kinds of contamination and dangers caused by materials.
The following is standard personal protective equipment used in laboratories according to their needs:
- Laboratory coat : A laboratory coat functions to protect the body from splashes of dangerous chemicals. There are two types, namely disposable lab coats and reusable lab coats. Disposable lab coats are generally used in biology and animal laboratories, while reusable lab coats are used in chemistry laboratories.
- Safety glasses : Splashes of chemical or hot solutions can harm the eyes of people working in the laboratory. Therefore, special glasses must be used that are resistant to potential chemical and heat hazards. These glasses are divided into two types, namely clear safety glasses and clear safety goggles. Clear safety glasses are ordinary safety glasses used to protect the eyes from splashes of chemical solutions or dust. Meanwhile, clear safety goggles are used to protect the eyes from chemical splashes or dangerous chemical reactions.
- Shoe : Sandals or sandals are prohibited when working in the laboratory. Because they cannot protect the feet when solutions or chemicals are spilled. Ordinary shoes are generally sufficient for use as protection. However, in large corporate laboratories, the shoes used are safety shoes that are resistant to fire and certain pressures. Apart from that, sometimes plastic shoe covers are also provided to keep the laboratory clean if the shoes are used to leave the laboratory.
- Mask : As the name suggests, a face shield is used to protect the face from heat, fire, and splashes of hot material. This tool is commonly used when taking laboratory equipment that is heated in a high-temperature furnace, melting soil samples in laboratory-scale melting equipment, or taking equipment that is heated in an autoclave.
- Gas mask : The chemicals or chemical reactions produced can emit dangerous gases. Therefore, a gas mask is very suitable to use so that dangerous gases are not inhaled. Judging by the type, gas masks can be ordinary gas masks made of cloth or special gas masks equipped with gas suction material. Ordinary gas masks are generally used for general purposes, for example, making standard solutions. Meanwhile, special gas masks are used when using solutions or chemicals that contain dangerous gases, for example, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and sulfide acid.
- Gloves : Gloves protect your hands from splashes of chemical solutions that can make your skin itch or blister. The types of gloves used in the lab are usually made from natural rubber, nitrile, and neoprene. Regarding gloves made from natural rubber, some are equipped with special powder and some are not. This powder is generally made from starch and functions to lubricate gloves, so it is easy to use.
- Ear protector : The last piece of personal protective equipment is ear protection. This tool is commonly used to protect the ears from noise emitted by certain equipment, for example, autoclaves, soil sample grinders (crushers), sonicators, and glassware washers that use ultrasonics.
Personal protective equipment in Biosafety Level (BSL) laboratories is adjusted to the BSL level. The higher the BSL level, the higher the level of security for laboratory staff and the environment. The following are the differences in safety equipment in each BSL laboratory:
| Risk Group | BSL | Laboratory Type | Laboratory Practice | Safety Equipment |
| 1 | Basic , BSL 1 | Training, research | GMT (Good Microbiological Technique) | – |
| 2 | Basic , BSL 2 | Health care, diagnosis, research | GMT+ protective clothing, biohazard sign | BSC for aerosol potential |
| 3 | Containment , BSL 3 | Specific diagnosis, research | Level 2 + special clothing, limited access, directional air flow | BSC + / primary devices for all activities |
| 4 | Maximum Containment , BSL 4 | Dangerous pathogen unit | Level 3 + airlock entry, shower exit, special waste disposal | Class III BSC +++++ |
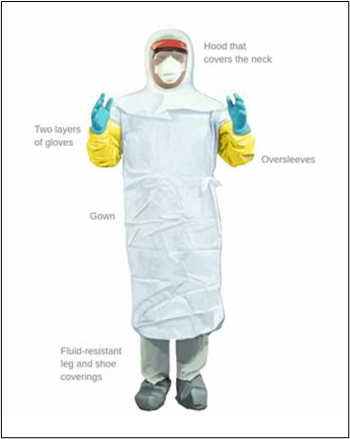 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Biosafety Level 3 Laboratories. Protective clothing must be solid-front gowns, head coverings, and shoe covers. Gloves with 2 layers, head covers, and shoe covers Gloves are double-layered. Masks and glasses must be worn (source: Labster Theory, 2018).
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Biosafety Level 3 Laboratories. Protective clothing must be solid-front gowns, head coverings, and shoe covers. Gloves with 2 layers, head covers, and shoe covers Gloves are double-layered. Masks and glasses must be worn (source: Labster Theory, 2018).
Safety in the laboratory is not an option but a necessity. Many materials and agents, hazardous substances, dangerous tools, and experimental procedures used in laboratories can cause serious injury if not handled properly. Therefore, every laboratory must have strict safety standards that are followed by all members:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) : Using PPE such as gloves, protective glasses, lab coats, and special shoes is an important step in protecting yourself from potential dangers.
- Material Management : Handling, storage, and disposal must be carried out in accordance with the correct procedures and in compliance with applicable regulations.
- Routine Inspection : Regular checks of laboratory equipment and safety facilities should be carried out to ensure that they are functioning properly.
- Safety Training : All laboratory team members must undergo regular safety training and understand emergency evacuation procedures.
It is important to remember that safety and ethics in laboratories do not just affect the scientists and researchers within them. The results of laboratory research can have a major impact on society as a whole. When safety and ethical standards are implemented correctly, it helps to:
- Preventing Public Health Risks: Good safety avoids potential risks of environmental pollution or negative impacts on human health.
- Leads to more credible discoveries: Strong ethics in research increase public trust in research results.
- Driving continuous innovation: Safe and ethical laboratories provide a strong foundation for continuous innovation and technological development.
Recent challenges to maintaining safety in laboratories have become increasingly complex as technology advances and biosecurity risks evolve. One of the main challenges is the use of new technologies in research and laboratory experiments. Although these technologies provide major advances in scientific knowledge, they also bring new risks. For example, the use of robotics and artificial intelligence in laboratory experiments can lead to potential technical failures that could endanger the safety of laboratory staff.
Apart from that, biosecurity risks are also becoming an increasingly pressing issue. Events such as incidents of leakage of hazardous biological materials or misuse of pathogenic agents for negative purposes are of major concern. Laboratories working with potentially deadly organisms must adhere to strict protocols to prevent leaks or unauthorized access. This includes increasing monitoring of physical access to laboratory facilities and strengthening data security measures to protect sensitive information about biological agents.
To overcome these challenges, laboratories must continue to implement best practices in risk management and safety. This includes staff training, monitoring new technology, emergency planning, and collaboration with authorized agencies to ensure that the laboratory operates according to the highest standards in terms of safety and biosecurity.
Safety in the laboratory is a top priority in scientific research, and keeping this safety relevant to evolving technologies and evolving risks is a critical task.
To overcome increasingly complex laboratory security challenges, there are several solutions that can be implemented.
- There is a need to further improve the training and awareness of laboratory staff regarding security principles. This involves regular training in risk management, handling of hazardous materials, and emergency safety measures. Laboratory staff must also have a strong understanding of the protocols and procedures that apply within the laboratory.
- The use of advanced technology to improve laboratory security can be a solution. For example, the use of advanced video surveillance systems and artificial intelligence technology to detect unexpected changes in the laboratory environment can help prevent security incidents. Additionally, robust information security software and systems should be used to protect sensitive data and guard against unauthorized access.
- Collaboration and partnership with national and international security agencies are important components of maintaining laboratory security. This can assist in the exchange of information about potential threats as well as provide up-to-date guidance when it comes to laboratory security.
Strict regulations and strict law enforcement must be implemented to ensure that laboratories comply with existing safety standards. Strict sanctions for security violations should be implemented to incentivize laboratories to prioritize security. By implementing these solutions, we can improve laboratory security, maintain the safety of laboratory staff, and prevent potential incidents that could have a negative impact on the environment and wider society.
Bibliography :
- Recognize the Dangers of Working in a Laboratory, UNAIR News 2019
- Laboratory Management, Sulistyani Puteri Ramadhani, 2020
- Science and Technology Journal of Proceedings Series No. (4) (2019), ISSN (2354-6026)
- Andri Setiawan, Instrumentation & Biomolecular Technique, Biosafety Biosecurity Risk Assessment, 2018
- IB Amertha Putra Manuaba, Procedures for Using Personal Protective Equipment Biosafety Level 1 and Level 2, Directory of Open Access Journals, 2016
- Popi Hadi Wisnuwardhani, BIOSAFETY LABORATORY PRACTICES: GENERAL WORK SAFETY GUIDELINES IN BIOSAFETY LEVEL LABORATORIES, Therapeutic Protein and Vaccine Laboratory Biotechnology Research Center – LIPI, BioTrends Vol.9 No.2 of 2018

Leave a Reply